 ).
).
In this Topic Hide
This topic explains how to complete the Counters tab when editing an item in the equipment hierarchy.
Counters are used to specify the total quantity of product manufactured. The quantities recorded are assigned to a counter type. The standard counter types are Good, Scrap and Total which are used to calculate the OEE.
Counters receive the values via a Collector which is used to import data automatically from the production line. Each Counter needs to be set up for each machine separately specifying the tag required.
1. Select the Counters tab.
A list of the existing Counters is shown.
2. Click the add icon ( ).
).
The following dialog opens.
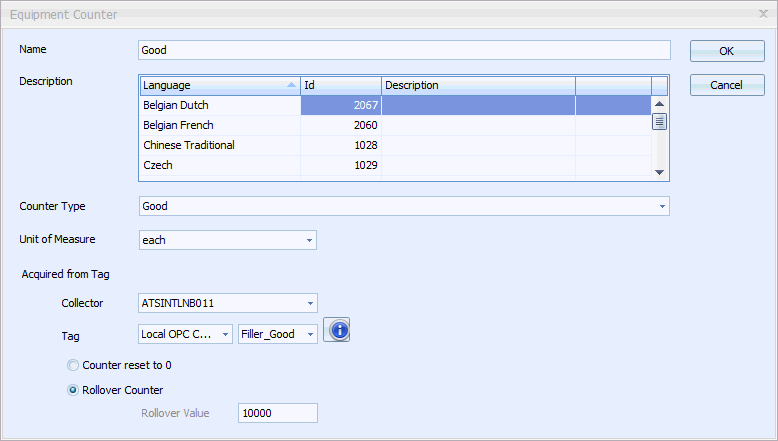
3. Select the Counter Type.
For more information on counter types see here.
4. Select the Unit of Measure that the counter will use.
5. If the Counter will be Acquired from Tag:
a. Select the Collector from which the Tag will be read.
b. In the Tag line select the channel.
c. Select the equipment tag.
d. Select whether the counter should reset to 0 after every value is received or whether it should keep adding up and then rollover at a specific value. See below for more information.
6. Click OK.
The counter is added to the list.
There are two different ways in which the values received from the equipment are recorded. The counter must be set up to match the method of counting used by the equipment.
The equipment can reset the value to zero at any time. It is assumed that it is sending the last value it has to ATS Intelligence before it resets.
If a new value received from the equipment is greater than the previous value received then it will simply store the new value. If the new value is less than the previous value then it will add the new value to the previous value.
With this method you have to specify the value at which the counter rolls over and returns to zero.
If a new value received from the equipment is greater than the previous value received then it will simply store the new value. If the new value is less than the previous value then it will add the value at which the counter resets to zero to the new value.
For example, let's say a piece of equipment has a rollover value of 100 and sends the following values to ATS Intelligence - 35, 75, 90, 20, 40. They would be recorded in ATS Intelligence as follows:
| Value received | Value stored |
| 35 | 35 |
| 75 | 75 |
| 90 | 90 |
| 20 | 130 (= 20 + rollover value) |
| 40 | 170 |