-
Select the Plants tab.
Click Stations.
A list of the existing stations is displayed.
Select Data Collect from the drop-down list above the right-hand pane.
If you are looking for existing Data Collect stations you can also filter using the Area drop-down list.
Click the add icon (
 ) below the right-hand
pane.
) below the right-hand
pane.The station creation dialog opens.
Select the Port Handlers tab.
Data Collect has the ability to receive messages via RS-232 serial ports to handle a number of tasks – most importantly, the ability to log in a user and to switch units (via serial number or any of the three identifiers). The most common use of this capability is the attachment of RS-232 bar code scanners.
To create or edit Serial Port Handlers:
Click the add icon (![]() ).
).
Select TCP/IP or RS-232.
TCP/IP
The following dialogue is displayed:
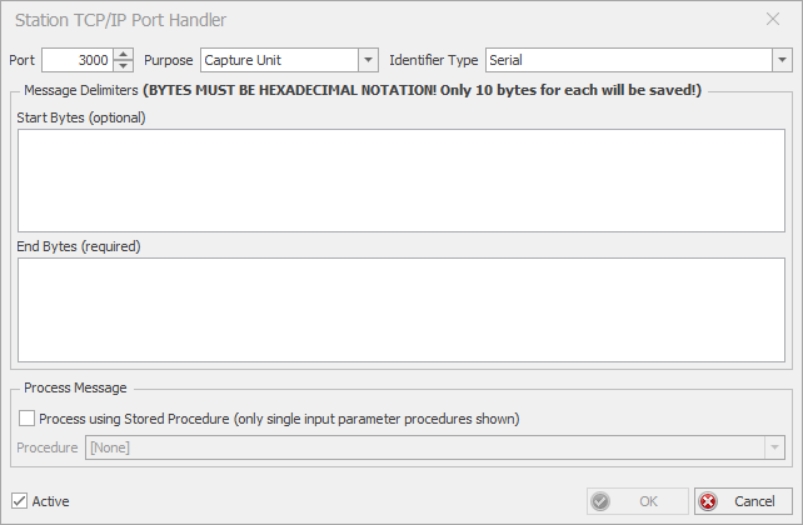
Enter the following details:
Port: The port number.
Purpose: The purpose of the port handling. Select either Capture Unit or Capture User.
Capture Unit: Select an identifier type from the Identifier Type drop down box or specify a stored procedure in the Procedure drop down box.
Capture User: Specify a stored procedure in the Procedure drop down box.
Start bytes: The character it is expecting the message to start with (optional).
End bytes: The character it is expecting the message to end with.
Hex editor is used for the start message and end message strings. This allows for the entry of non-printable characters such as a carriage return (0x1A).
Process using Stored Procedure. Place a tick in the check box to specify a store procedure.
Procedure: Select a stored procedure to handle the port from the drop-down list.
Example stored procedure if Capture Unit is selected:
CREATE procedure [custom].[custom_identifier_serial]
@identifier nvarchar(50)--serial
as
begin
declare @unitID int,
@identifier_type_id int
select @identifier_type_id = (select identifier_type_id from unit_identifier_types where code = 'SERIAL')
select @unitID = (select unit_id from unit_identifiers where identifier_type_id = @identifier_type_id and identifier = @identifier)
return @unitID
end
GO
If Capture User is selected and a stored procedure is used, a "user code" must be returned and not a user id as in the past. This user code is the "EXTERNAL CODE" value from Security Manager for the user.
Click OK.
The port handler is added to the list.
Now go to the Top Concerns tab.
RS-232
The following popup appears:

Enter the following details:
Port: The port number.
Purpose: The purpose of the port handling. Select either Capture Unit or Capture User.
If Capture Unit is selected a stored procedure should be used that knows the type of identifier to use.
BPS: Bits per second transfer rate.
Data Bits: Number of bits per character.
Stop Bits: Number of bits to detect end of character.
Parity: Method of detecting errors in transmission (None, Odd or Even).
Start bytes: The character it is expecting the message to start with (optional).
End bytes: The character it is expecting the message to end with.
Hex editor is used for the start message and end message strings. This allows for the entry of non-printable characters such as a carriage return (0x1A).
Process using stored procedure: Activate if you wish to use a stored procedure to handle the port. If you do you must then select a stored procedure from the drop-down list.
Click Save.
The port handler is added to the list.
Now go to the Top Concerns tab.
Common ASCII Character Codes
|
Character |
Hexadecimal |
Decimal |
|
Form Feed |
0C |
12 |
|
Carriage Return |
0D |
13 |
By default the port handlers look for the following:
|
Program Task |
Expected Value |
|
Serial |
Serial Number |
|
Identity #1 |
Identity #1 |
|
Identity #2 |
Identity #2 |
|
Identity #3 |
Identity #3 |
|
User |
User Code (not password!) |
If the above information is not available, other information may be passed in and processed by a stored procedure with two parameters:
Unit ID isValue: data available from RS-232 port.
ID: returned for everything except User Program Task. User Program Task returns a User ID.
Stored Procedure
Below is an example for creating a stored procedure for a station port handler.
drop procedure if exists custom.custom_find_unit_by_serial
go
create procedure custom.custom_find_unit_by_serial
(
@identifier nvarchar(50)
)
as
begin
declare @unitID int
-- Always do a 'top 1' and order by unit_id descending
-- so that you get the newest unit and protect against
-- the possibility of duplicate identifiers
select top 1 @unitID = unit_id
from unit_identifiers ui join unit_identifier_types ut
on (ui.identifier_type_id = ut.identifier_type_id)
where ui.identifier = @identifier
and ut.code = 'SERIAL'
order by unit_id desc
if (@@rowcount = 1)
begin
-- Return unit id
return @unitID
end
return -1 -- Could not find unit!
end
go