In this topic: Hide
All your batches, views, and collected data are stored in a Microsoft Access 2000 compatible ‘JET’ database. If necessary you can use Microsoft Access as a supplementary tool for report generation or even data entry.

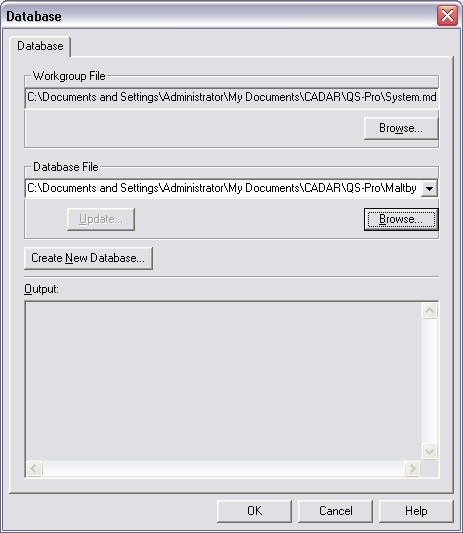
ATS SPC’s Database dialog provides functions to select a database file to use, to create a new database file, and to update a database from an earlier version of ATS SPC. It also shows the current workgroup database file and gives the opportunity to change that too if necessary.
The pathname shown under ‘Workgroup File’ is that of the security database containing details of users, groups and passwords for logging on to ATS SPC. The pathname shown under ‘Database File’ is that of the database ATS SPC is currently using. You should back up both of these files regularly to avoid embarrassing data loss in the event of an unforeseen mishap. The database file in particular changes every time someone enters or deletes data, or makes any changes to batches, features, control limits… almost anything at all in ATS SPC – and should be backed up every day.
If you have any open batches ATS SPC will simply show you the path to the current database file. You cannot change this while you have batches open.
1. If you have any open batches, close them.
2. Choose Database from the Tools menu.
3. Press [Alt+N] or click the New Database button.
4. ATS SPC asks if you want to create a signed or unsigned database. Click the appropriate button.
5. In the Create Database dialog, choose a folder and name to save the new database file. Press the Enter key or click the Save button.
ATS SPC creates a database file and populates it with tables and other required objects. It should finish by saying ‘Database Created OK’.
6. Press the Enter key or click the OK button to use the new database.
1. If you have any open batches, close them.
2. Choose Database from the Tools menu.
3. Type in the pathname to the database file you want to use or click the Browse button and find the required database file using the Open Database dialog. NB. If you have used the database before it may still be shown in the recent database list – click the arrow button on the right of the database box to drop down the list.
4. Press the Enter key or click the OK button to use the selected database.
If ATS SPC reports that the database you have chosen is from an earlier version you can update it in most cases…
See Update an Early Version Database
If the database you have chosen is signed you must log on to it using a valid user name and password.
Assuming you have just selected a database and received a warning that it is an earlier version…
1. Answer Yes to the question ‘Do you want to configure your database now?’
2. Back in the Database dialog press [Alt+U] or click the Update button.
3. ATS SPC will check each table and other object in the database and update it to the latest standard. If all goes well it will report ‘Database Updated OK’. Note that updating a database from ATS SPC prior to version 4.0 will result in an unsigned database.
4. Press the Enter key or click the OK button to start using the updated database.
In order to meet the requirements of traceability and data security standards such as 21CFR part 11, ATS SPC implements ‘hashing’ and ‘signing’ for batches and for data and other data-related records.
When such a record is written to the database ATS SPC marks it with the user name of the currently logged on user and calculates a hash value from all the elements of the record. This hash value is, to all intents and purposes, unique to the particular record. If anyone makes a change to the record the hash value will no longer be valid and the change is therefore easily detectable.
While this in itself does not make ATS SPC “21CFR compliant” it does allow it to be used in a 21CFR compliant working environment. (It is important to realise that a software package or other single product cannot be “21CFR compliant”. It is the working environment that must be compliant and this may demand 21CFR friendly products such as ATS SPC.)
If you need to work to a traceability standard you should use a signed database, otherwise use an unsigned one. Working in a signed database gives rise to the following restrictions…
1. Batches must be signed before you can collect data into them.
2. Once a batch has been signed, you cannot make any design changes to it.
3. You cannot delete signed batches.
4. While you can delete data from a signed batch the deleted data is retained in the database for future reference. The time/date and user ID of the user deleting the data is also recorded.
5. Logon restrictions apply