CM4D Data Terminology
The CM4D applications use terminology common throughout the product but may not be familiar to you as a user of CM4D Peruse. Review the following information to familiarize yourself with some of the terms used to describe data as it relates to CM4D.
Routines
A Routine is the measurement plan, typically related to a series of data collection steps that occur together, such as a run of samples for a specific part. One Routine normally refers to one part.
A group of Features and Samples loaded from the database. Routines are defined by the data files received from measurement devices.
Features
A Feature is a collection of characteristics that relate to the data collection or sampling process. Features will typically have one or more characteristics that represent the Nominal (or designed) values and Actual (or measured) values. CM4D derives the Feature type by looking at the characteristics of a feature, and if it meets certain criteria, it will define it as one of the feature types in the Feature Types table below.
Characteristic
A Characteristic is supporting information for the Feature, a measurable dimension or parameter of a feature such as a nominal X value, or an actual Y value.
A feature such as a point will generally have XYZ and IJK nominal data. A hole, however, will also have a diameter.
Samples
A Sample is the actual measurement of a Feature Characteristic.
Processes
A Process is what is being measured, or a single Characteristic of a Feature. Processes include information such as Nominals, Limits, and other information related to the process.
Results
The Results are a dimension of the Process, or the actual data obtained from the measurement. Results include information for investigation and analysis, such as
Deviation Types
The actual measurement data values can be displayed as either Absolute (Actual), Deviation or Car Deviation.
- Absolute - The actual measurement value stored in the database. This value is not changed in the database if you choose to display the data as a deviation.
- Deviation - The difference between the actual measurement value and the nominal value (actual minus nominal). This value is not stored in the database but is calculated as needed.
- Car Deviation - Calculated the same way as Deviation, but it only applies to XYZ values. This deviation type changes the sign of the deviation value if the nominal value is negative by assuming that the center of the part is at [0,0,0]. Essentially, choosing to display data as Car Deviation turns Left/Right to In/Out.
| Vehicle | Nominal Value | Absolute (Actual) | Deviation | Car Deviation |
| Car A - Right Door | +100.0 | +100.2 | +0.2 +100.2 - (+100.0) = +0.2 | +0.2 +100.2 - (+100.0) = +0.2 |
| Car A - Left Door | -100.0 | -100.2 | -0.2 -100.2 - (-100.0) = -0.2 | +0.2 +100.2 - (+100.0) = +0.2 |
| Car B - Right Door | +100.0 | +99.2 | -0.8 +99.2 - (+100.0) = -0.8 | -0.8 +99.2 - (+100.0) = -0.8 |
| Car B - Left Door | -100.0 | -99.2 | +0.8 -99.2 - (-100.0) = +0.8 | -0.8 +99.2 - (+100.0) = -0.8 |
Feature Types
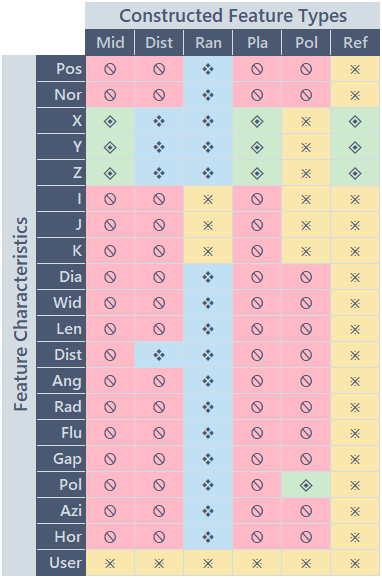
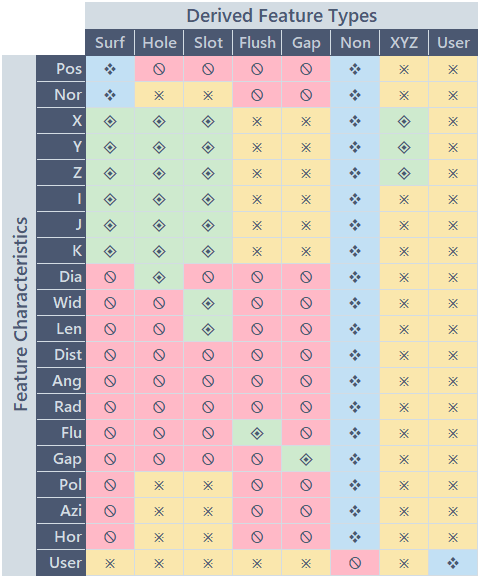
Feature Type identifies the kind of dimension which was measured. There are two categories of feature types in CM4D:
- Derived Features - Standard measurement dimensions (Surface, Hole, Flush, etc.) with data values which are input via data files processed into the database; type is determined automatically by CM4D based on present characteristics. Close Derived Feature Characteristics Criteria TableOpen Derived Feature Characteristics Criteria Table

- Constructed Features - Fabricated measurement dimensions (Distance, Midpoint, etc.) with data values which are calculated by CM4D; type is determined manually by Users when feature is created. Close Constructed Feature Characteristics Criteria TableOpen Constructed Feature Characteristics Criteria Table